Thyroid Cancer Treatment: Your Guide to the Best Options for a Cure
Thyroid Cancer Treatment: Your Guide to the Best Options for a Cure
Thyroid cancer treatment encompasses a range of strategies tailored to the specific type and stage of the disease, as well as individual patient factors. Understanding these treatment modalities is crucial for patients and their families as they navigate the complexities of thyroid cancer.
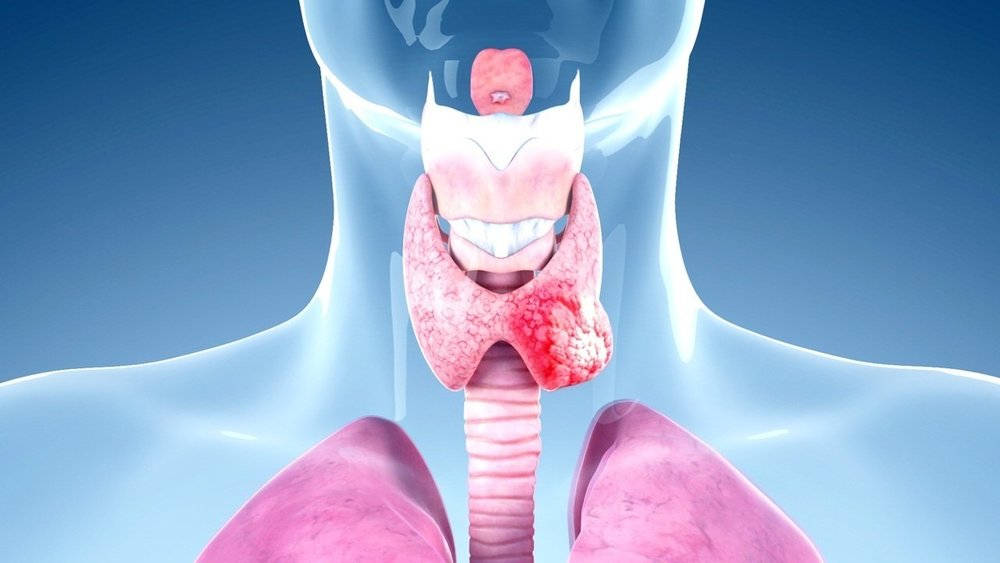
Thyroid Cancer Treatment Overview
The primary goal of thyroid cancer treatment is to eliminate cancerous cells while preserving normal thyroid function when possible. Treatment options vary based on the type of thyroid cancer—such as papillary, follicular, medullary, or anaplastic—and its progression. Common treatments include surgery, radioactive iodine therapy, and hormone therapy.
Surgical Options in Thyroid Cancer Treatment
Surgery is the most effective treatment for thyroid cancer, aiming to remove the tumor and affected tissues while minimizing the risk of recurrence. The extent of surgery depends on the cancer's size, location, and type.
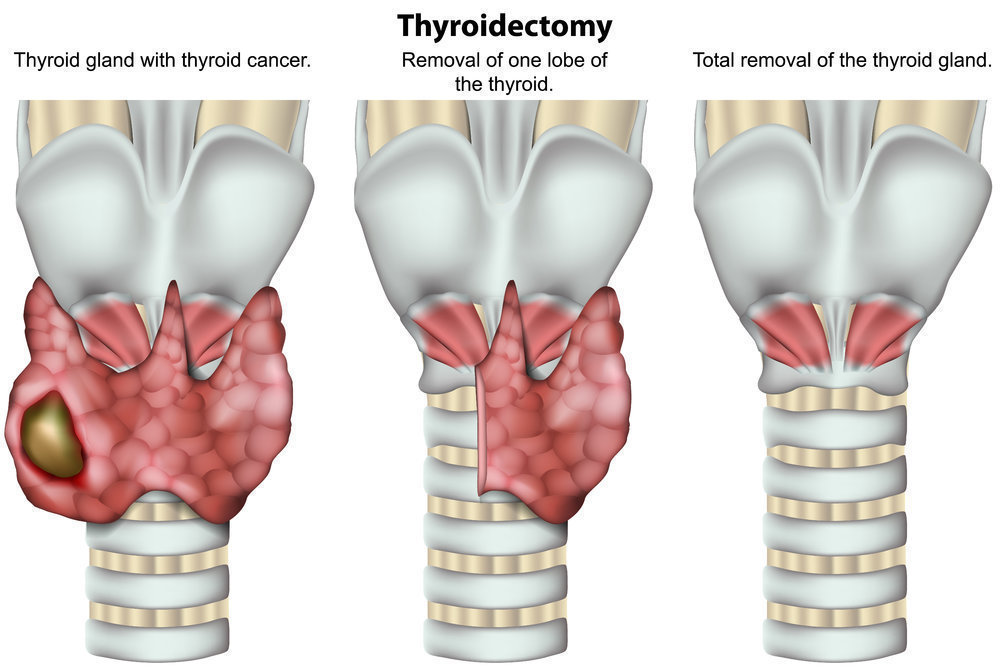
- Thyroid Lobectomy: This procedure involves removing one lobe of the thyroid gland and is typically considered when the cancer is confined to a single lobe and is relatively small. A lobectomy may be sufficient for certain low-risk cancers, preserving partial thyroid function.
- Total Thyroidectomy: In cases where cancer is present in both lobes or is more aggressive, a total thyroidectomy—removal of the entire thyroid gland—is performed. This approach reduces the risk of recurrence but necessitates lifelong thyroid hormone replacement therapy.
- Lymph Node Dissection: If cancer has spread to nearby lymph nodes, surgical removal of these nodes is essential. Comprehensive evaluation and removal of affected lymph nodes can prevent further metastasis and improve outcomes.
The Importance of Protecting the Parathyroid Glands During Thyroid Surgery
The parathyroid glands, located adjacent to the thyroid, regulate calcium levels in the body. During thyroid surgery, preserving these glands is crucial to prevent hypocalcemia, a condition characterized by low calcium levels leading to muscle cramps and tingling sensations. Experienced surgeons take meticulous care to identify and protect the parathyroid glands during thyroidectomy procedures.
Incision and Scar Considerations
Concerns about scarring are common among patients undergoing thyroid surgery. Advancements in surgical techniques have led to smaller, well-placed incisions that align with natural skin creases, resulting in minimal and often inconspicuous scars. Postoperative care, including proper wound management and, if necessary, interventions like laser therapy, can further enhance scar appearance.
Robotic Thyroid Surgery
For patients who want to avoid a visible neck scar, robotic thyroid surgery is an advanced option. This technique, performed through an incision under the arm, eliminates the need for a neck incision. Robotic-assisted procedures allow for enhanced precision, reducing trauma to surrounding tissues and promoting a smoother recovery. Not all patients are candidates for robotic thyroid surgery, so consulting with an experienced thyroid surgeon is essential to determine suitability.
Radioactive Iodine Therapy in Thyroid Cancer Treatment
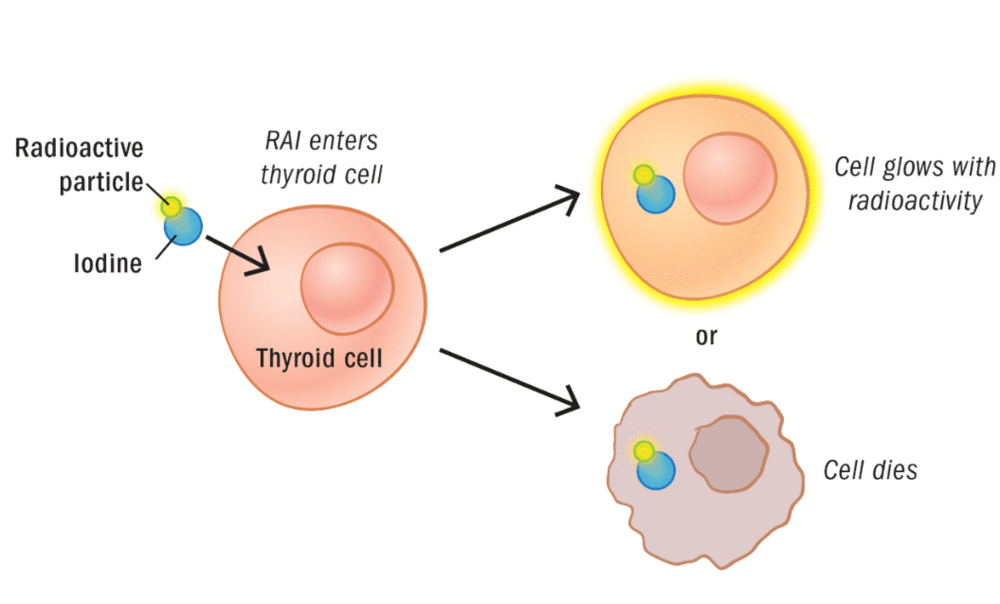
Radioactive iodine (RAI) therapy is commonly used after surgery, especially for papillary and follicular thyroid cancers. Since thyroid cells naturally absorb iodine, administering radioactive iodine helps destroy any remaining cancerous thyroid tissue without harming other parts of the body. This treatment reduces the risk of recurrence and is generally well-tolerated.
Hormone Therapy in Thyroid Cancer Treatment
After thyroidectomy, patients may require thyroid hormone replacement therapy to maintain normal metabolism. Additionally, suppressive doses of thyroid hormone can inhibit the production of thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH), which may otherwise promote the growth of any residual cancer cells. This dual role makes hormone therapy a cornerstone in thyroid cancer management.
Preventing Recurrence in Thyroid Cancer Treatment
While many patients achieve a cure with proper thyroid cancer treatment, recurrence is possible. In many cases, recurrence is due to an incomplete initial surgery, where an inexperienced thyroid surgeon leaves behind cancerous tissue. This is why selecting the right surgeon the first time is critical. A high-volume, expert thyroid surgeon can remove all cancerous tissue effectively, reducing the chances of recurrence and avoiding the need for a second surgery. If recurrence does occur, additional surgery, radioactive iodine therapy, or other treatments may be necessary.
Choosing the Right Surgeon for Thyroid Cancer Treatment
The success of thyroid cancer treatment significantly depends on the surgeon's expertise. High-volume thyroid surgeons—those performing numerous thyroid surgeries annually—tend to have lower complication rates and better patient outcomes. Patients are advised to research and select surgeons with extensive experience in thyroid procedures to ensure optimal care.
Why Choose the Clayman Thyroid Center?
The Clayman Thyroid Center is the highest-volume thyroid cancer surgery center in the United States, with a team of expert surgeons performing thousands of thyroid cancer surgeries each year. Their extensive experience and focus on thyroid cancer ensure that patients receive the best possible care with the highest cure rates and the lowest complication rates. Choosing a high-volume center like the Clayman Thyroid Center significantly reduces the risk of recurrence and improves long-term outcomes for patients diagnosed with thyroid cancer.
Additional Resources
- Become our patient by filling out the form at this link.
- Learn more about The Clayman Thyroid Center here.
- Learn more about our sister surgeons at the Scarless Thyroid Surgery Center, Norman Parathyroid Center, and Carling Adrenal Center
- Learn more about the Hospital for Endocrine Surgery.